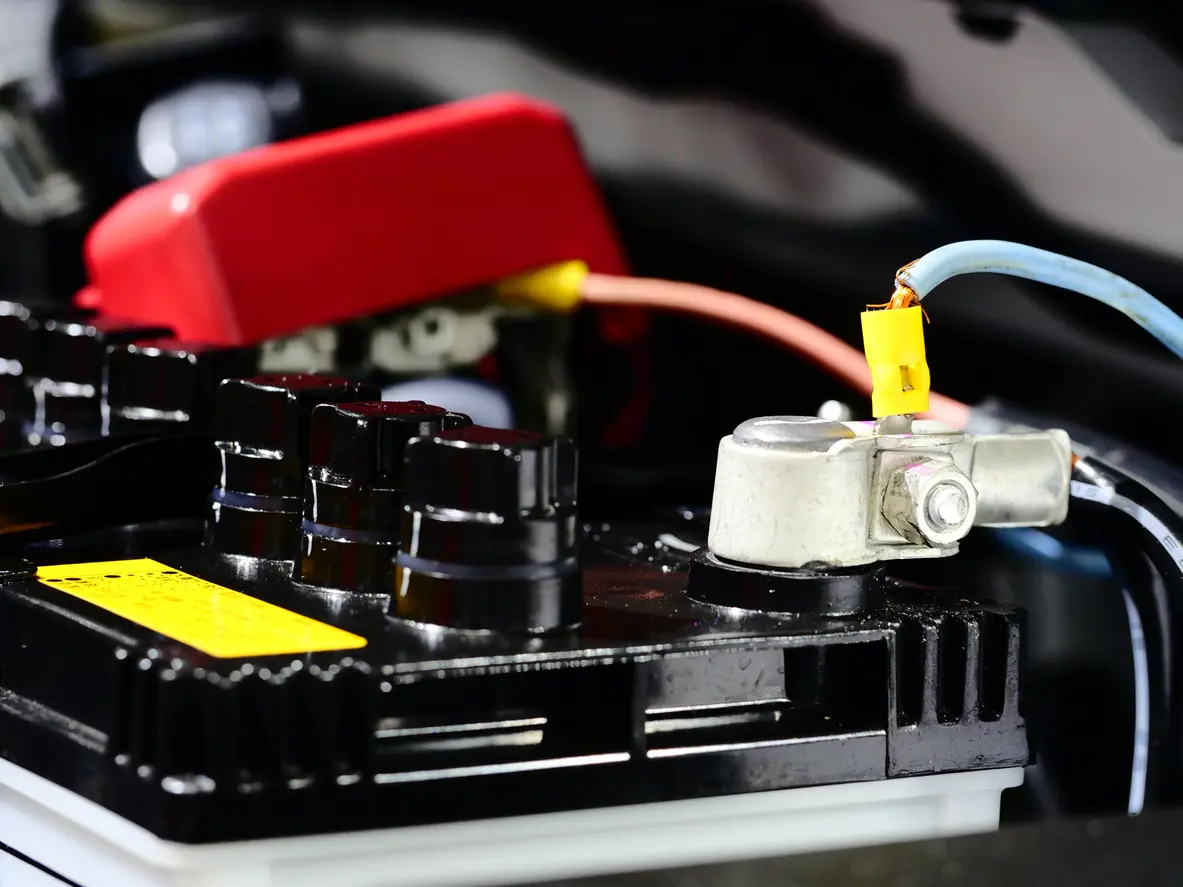
EV and hybrid batteries
EVs and hybrids contain both a high-voltage battery and a 12 V auxiliary battery. Each battery powers separate systems within the vehicle.
The high-voltage (HV) battery is the lithium-ion battery that powers several essential functions, including the propulsion system, regenerative braking, and climate control. It’s much larger than the 12 V battery.
The 12 V auxiliary battery is the same lead-acid battery found in traditional gas-powered vehicles. It powers low-voltage operations including dashboard displays, navigation, windows, airbags, ABS, interior lighting, the radio, and USB ports. Although the HV battery charges it, the auxiliary battery supplies power to the starter and is therefore responsible for turning on an EV or hybrid motor.
Why two batteries?
If your HV battery powered your car’s electronics, it would fry them. However, the 12 V system also ensures that critical safety systems remain operational even if the HV battery fails. This sharing of functions results in improved energy management.
Unlike in traditional vehicles, the auxiliary battery is not charged by an alternator but instead by a DC/DC converter (the inverter). This component changes the voltage level of one source of direct current to another, acting as a translator between the two batteries so the HV battery can charge the 12 V battery.
What does this mean for jump-starting an EV or hybrid?
Because the 12 V auxiliary battery powers the vehicle’s start-up process, this is the battery you need to jump-start, not your vehicle’s primary battery.
Do not attempt to jump-start the HV battery under any circumstances. The amount of electricity running through it can cause serious injury and even death.
How to jump-start an EV or hybrid vehicle
There are two ways to jump-start an EV or hybrid. In both cases, you must complete these two steps first:
Step 1: Locate the 12 V auxiliary battery or jump-start points. Common locations for the auxiliary battery include the engine compartment, below the rear seats, or in the trunk of your vehicle. Some vehicles are equipped with jump-start terminals located under the hood for easier access. Consult your owner’s manual for exact details.
Step 2: Use a gas-powered vehicle or portable jump starter to boost the auxiliary battery. You cannot jump-start an EV or hybrid using another EV. The 12 V battery systems in these vehicles are not designed to perform this operation. If using a gas-powered car for your jump start, park the vehicles close enough for the cables to connect, but ensure the vehicles themselves are not touching.
To jump-start your EV or hybrid with the battery from a gas-powered vehicle, do the following:
Step 3: Turn off both vehicles.
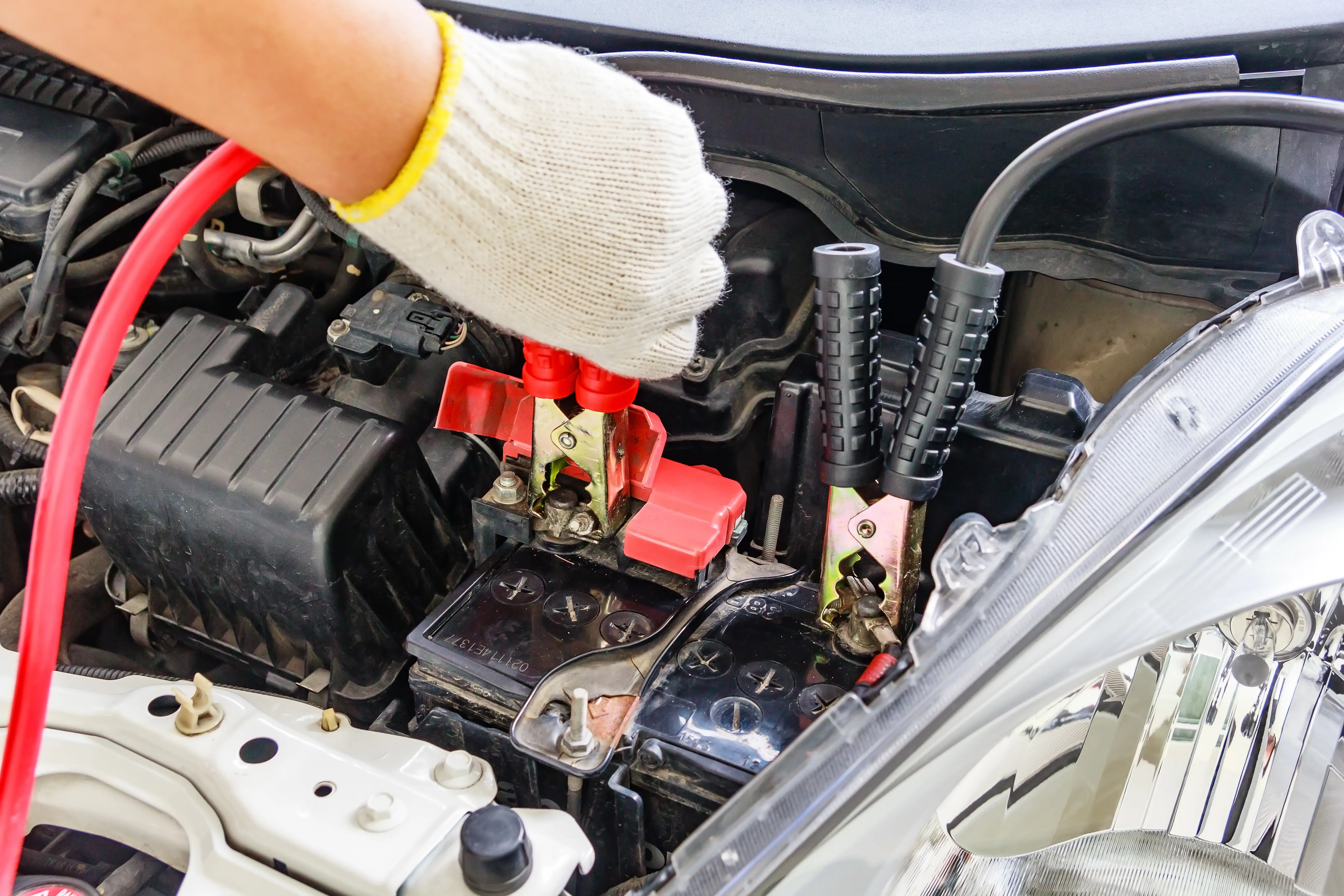
Step 4: Connect the positive terminals using the red clamps. Attach one red clamp to the positive (+) terminal of the EV or hybrid’s auxiliary battery, then attach the other red clamp to the positive (+) terminal of the working battery.
Step 5: Connect the negative terminal to a grounding connection. Attach one black clamp to the negative (-) terminal of the working battery. Attach the other black clamp to an unpainted metal surface on the EV or hybrid, such as a bolt or bracket, to ground the connection. Do not connect it directly to the negative terminal of the dead battery.
Step 6: Turn on the gas-powered car.
To jump-start your EV or hybrid using a jump starter, follow these steps:
Step 3: Turn off your EV or hybrid and the jump starter.
Step 4: Connect the red clamp from the jump starter’s cables to the positive (+) terminal on your EV or hybrid’s auxiliary battery.
Step 5: Connect the black clamp to an unpainted metal surface on the EV or hybrid that is far away from the battery. Do not connect this clamp to the auxiliary battery.
Step 6: Turn on the jump starter.
The remainder of the process is the same for both methods.
Step 7: Wait 5 minutes while connected to the EV or hybrid.
Step 8: Try starting the EV or hybrid. If it does not start immediately, wait a few more minutes, then try again.
Step 9: Once the EV or hybrid has powered on, disconnect the jumper cables by following steps 3–5 for your jump-start method in reverse.
Step 10: Let the EV or hybrid run for at least 20 minutes to allow the auxiliary battery to recharge.
At the next available opportunity, recharge your jump starter so that it’s ready to go should you run into this situation again.
When to see a technician
If the auxiliary battery in your vehicle dies frequently, there may be deeper issues with your charging system or DC/DC converter. Some EVs and hybrids will display error messages to tell you when the 12 V auxiliary battery is running low. If there is an issue with your high-voltage battery, a jump start won’t help.
If you get frequent error messages, the 12 V battery consistently struggles to stay charged, or you suspect that your high-voltage battery itself is the cause, chat with a knowledgeable technician at your nearest NexDrive service centre.
How battery thermal management systems work
Your EV’s battery thermal management system helps to improve battery performance and to keep the battery at a safe temperature. Learn how.

How to maintain your EV’s filters
Gas-powered and electric vehicles (EVs) sometimes have different filter requirements. Learn what filters EVs have and how to maintain them.

How to Jump-Start an EV battery
Dealing with a dead battery is always a nuisance. But what if you have an electric vehicle? Learn how to jump-start a dead EV with this guide.