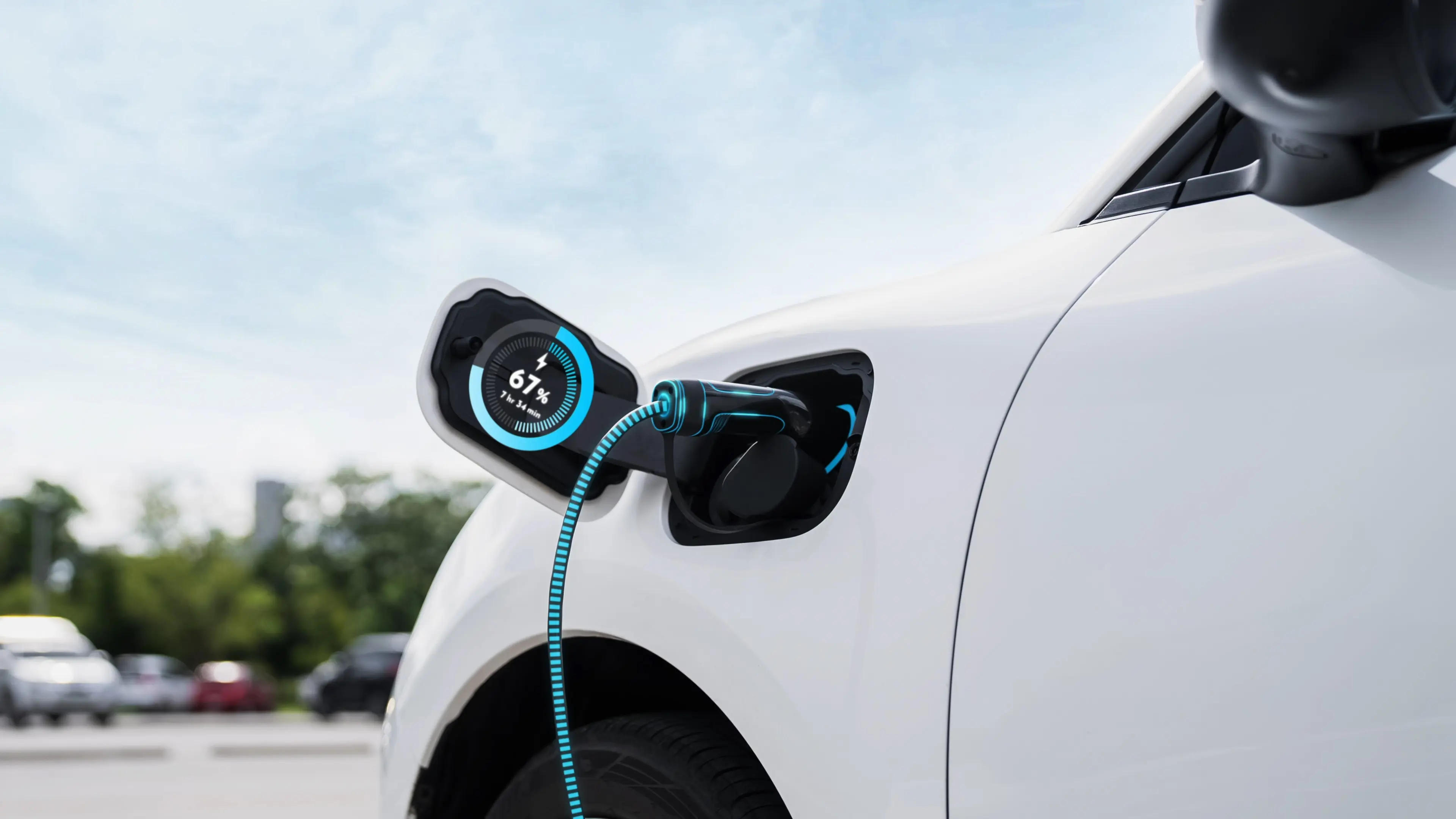
These questions focus on fully electric vehicles (BEVs). The answers may differ slightly for hybrids (HEVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs).
How Long Do EV Batteries Last?
EV batteries are much sturdier than regular ICE batteries. They’re built to last longer than the rest of the vehicle, meaning you shouldn’t need to replace one for at least 10 to 15 years.
You can help your EV battery last as long as possible by keeping the battery charged between 20% and 80% and avoiding driving, charging, and storing your vehicle in extremely hot or cold temperatures.
What Are EV Batteries Made Of?
The battery accounts for roughly 30-40% of an EV’s value. Most EVs run on lithium-ion batteries. The main materials in these batteries are lithium carbonate, nickel, manganese, graphite, and cobalt. These materials are used to create a positively charged cathode and a negatively charged anode.
What Are the Types of EV Chargers?
EV charging is categorized into three levels.
Level 1, also known as slow charging, uses an AC charger. Level 1 EV charging can be done from home using a standard 120-V outlet. It can take 40+ hours to charge a BEV to 80% from empty with a Level 1 charger. PHEVs can reach the same capacity in roughly 5-6 hours with Level 1 charging.
Level 2 is considered fast charging, and it’s the most common type of EV charging. It also uses an AC charger but requires a 240-V outlet. Most public charging stations are equipped with Level 2 chargers. You can also have one installed in your home. Level 2 charging usually takes between 5-10 hours to charge a BEV to 80% and 1-2 hours for a PHEV.
Level 3 rapid charging is the quickest way to charge up your EV. Using a DC charger (aka a supercharger), Level 3 charging can boost your BEV battery to 80% in 30-60 minutes (as quick as 15 minutes for a PHEV). Level 3 chargers are mostly for commercial use because of the power they draw, but you can find them in many public charging stations. Use an app to help you find charging stations as needed.
Although it’s the fastest option, frequent Level 3 charging can degrade your EV battery faster. Rely on Level 2 charging for your regular charging routine and keep Level 3 as an emergency option if needed.
How Long Does It Take to Charge an EV?
The time it takes to charge your EV will depend on the charging level you use, your specific vehicle type, make, and model, and the overall health of your battery.
Refer to your owner’s manual for more guidance on how long it should take to charge your EV based on its design.
How Often to Charge an EV?
Knowing when to charge your EV depends on your driving habits. For example, if your daily commute is less than 75 km, you can likely charge your vehicle every two or three days.
Those who use Level 1 chargers at home often plug their cars in overnight so they're always ready to go in the morning. If you use a faster charging method, you won’t need to follow the same schedule.
Pay attention to your EV’s battery capacity and charge it as needed to keep it between 20 and 80%. Continually charging your battery to 100% or regularly letting it die completely can damage the battery over time.
Where to Charge EVs?
EV charging stations are growing in numbers as more people switch out gas for electricity. You can often find them at supermarkets, in parking lots, and on the road near parks. Many public charging stations are free to use. If you do have to pay, your bill will be much lower than it would be at the gas pump. Various apps are also available to help you locate charging stations near you/along your route. If you’re planning a long journey, incorporate charging station stops to avoid range anxiety.
Maintaining Your EV
Keeping your EV properly charged is essential to its performance. Although EVs don’t require as much maintenance as regular cars, certain parts still need professional attention to keep them running their best.
For more information about EV charging and maintenance, chat with a knowledgeable expert at a NexDrive service centre.
Other Resources

Why do electric car tires wear out so fast?
EV tires experience increased tread wear because of instant torque and unsprung weight. Learn why electric vehicles lead to worn-out tires and how to extend the lifespan of EV tires with proper maintenance.
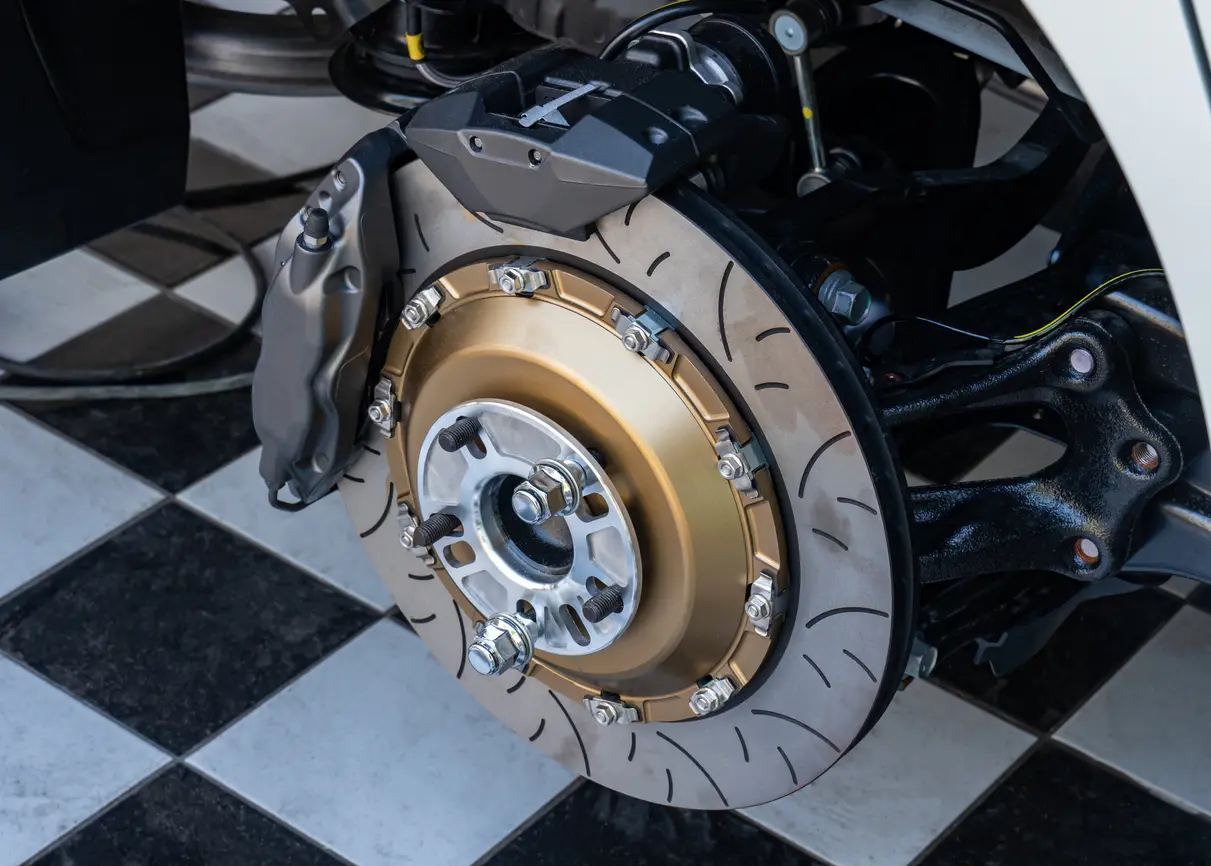

Why regenerative braking is bad for your brake pads
Regenerative braking improves energy efficiency, but can cause brake pad issues because of reduced mechanical brake use. Learn how to maintain your brake system and prevent costly repairs in this article.
Does an EV need regular general maintenance?
Although EVs require less maintenance than gas-powered vehicles, they still need regular care. Learn about battery health, brake maintenance, and more here.
