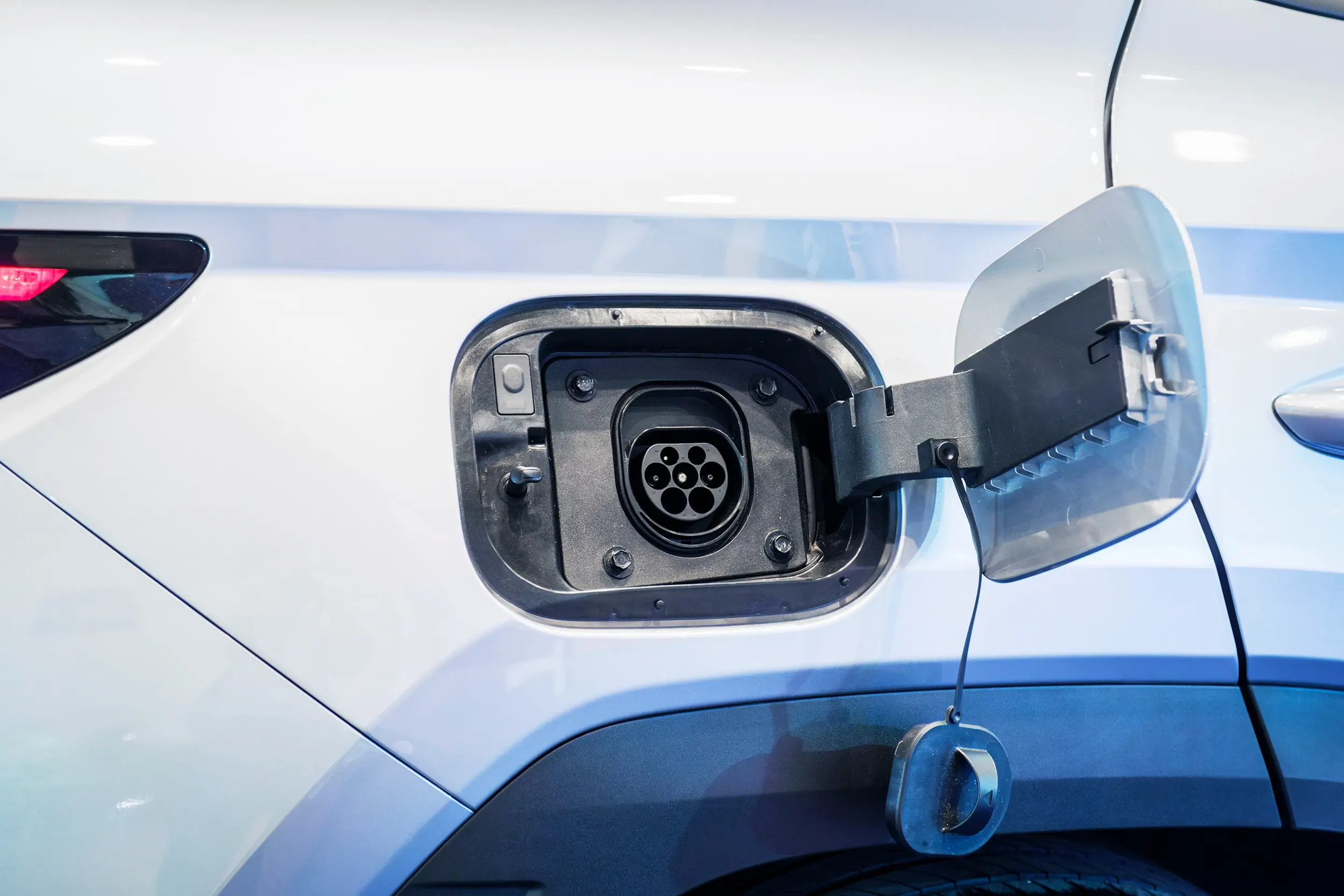
Electric Vehicle Charging Ports and Charging Systems
Several types of charging ports are available for charging electric vehicles. Each port is designed to meet specific charging standards and provide various charging speeds.
Type 1
One of the most common types of charging port is the Type 1 port, also known as the SAE J1772 port. This connector is widely used in North America and is compatible with most electric vehicles. It has five pins and supports both AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) charging. However, it offers relatively slower charging speeds than other connectors.
Type 2
Another popular port is the Type 2 port, also known as the IEC 62196 port. This port is commonly used in Europe and offers faster charging speeds than Type 1 ports. It has seven pins and supports both AC and DC charging. Type 2 ports also feature additional safety functions, such as the ability to cut the power supply when the port is unplugged.
DC Fast Charging
For faster charging, many electric vehicle owners opt for DC fast-charging ports. These ports, such as CHAdeMO and CCS (Combined Charging System) ports, are specifically designed for high-power DC charging. DC fast-charging ports can deliver a significant amount of energy to your electric vehicle, enabling rapid charge times. However, it’s important to note that not all electric vehicles support DC fast charging.
Common Problems With Charging Ports and Systems
Common problems associated with electric vehicle charging ports can range from minor inconveniences to major problems.
If your electric vehicle won’t charge, there could be several reasons. One of the most common problems is that the charging port isn't connecting properly to the charging cable. This may be due to a faulty latch or a damaged port. Another problem is that the charging port is not receiving power, which may be caused by a blown fuse or a faulty charging station. It’s important to consult your vehicle owner's manual and check for any error codes or warning lights before proceeding with troubleshooting.
When it comes to repairing electric vehicle charging ports, it is best to leave it to the professionals. Charging ports are complex electrical components. Diagnosis and repair require specialized knowledge and equipment, and attempting to repair the charging port yourself could not only void the vehicle warranty but also pose a safety risk. Our NexDrive technicians have the equipment and tools needed to safely diagnose and repair your vehicle’s charging port. Remember that electric vehicle high-voltage batteries are dangerous if not handled with proper safety equipment and professional materials.
Maintaining Your Charging System
Here are some important recommendations from our experts on maintaining your electric vehicle charging system:
- Never overcharge your electric vehicle: as a general rule, we recommend charging to 80–85% of battery capacity. This will avoid degradation, overheating and risks to this valuable component. As the charging port is made of solid plastic, it can be deformed by overheating.
- Never leave your cable on the ground: even if it’s in your garage, salt on the ground in winter can have a devastating effect on the port.
- Keep your charging station clean: wipe it regularly with a damp cloth to remove any dirt or debris that may have accumulated on the outside.
- Check the cable: continuous, periodic checking of the cable avoids most of the unpleasant surprises associated with failures resulting from damaged cables, loose ports and frayed wires.
- Check the charging port: regularly inspect the charging port for visible signs of damage, such as a bent port or loose plug. If you find any damage, consult a NexDrive center immediately to avoid further damage.
- Check for updates: check for updates to the charging station software and install them if necessary.
- Keep the charging cable in a safe place: make sure the charging port is kept in a safe place, away from water and other hazards.
Tips and Tricks

Why do electric car tires wear out so fast?
EV tires experience increased tread wear because of instant torque and unsprung weight. Learn why electric vehicles lead to worn-out tires and how to extend the lifespan of EV tires with proper maintenance.

Why regenerative braking is bad for your brake pads
Regenerative braking improves energy efficiency, but can cause brake pad issues because of reduced mechanical brake use. Learn how to maintain your brake system and prevent costly repairs in this article.
Does an EV need regular general maintenance?
Although EVs require less maintenance than gas-powered vehicles, they still need regular care. Learn about battery health, brake maintenance, and more here.

